根據 Nutcracker 機構的尺寸規格, 請設法算出 Piston 零件的有效運動範圍.
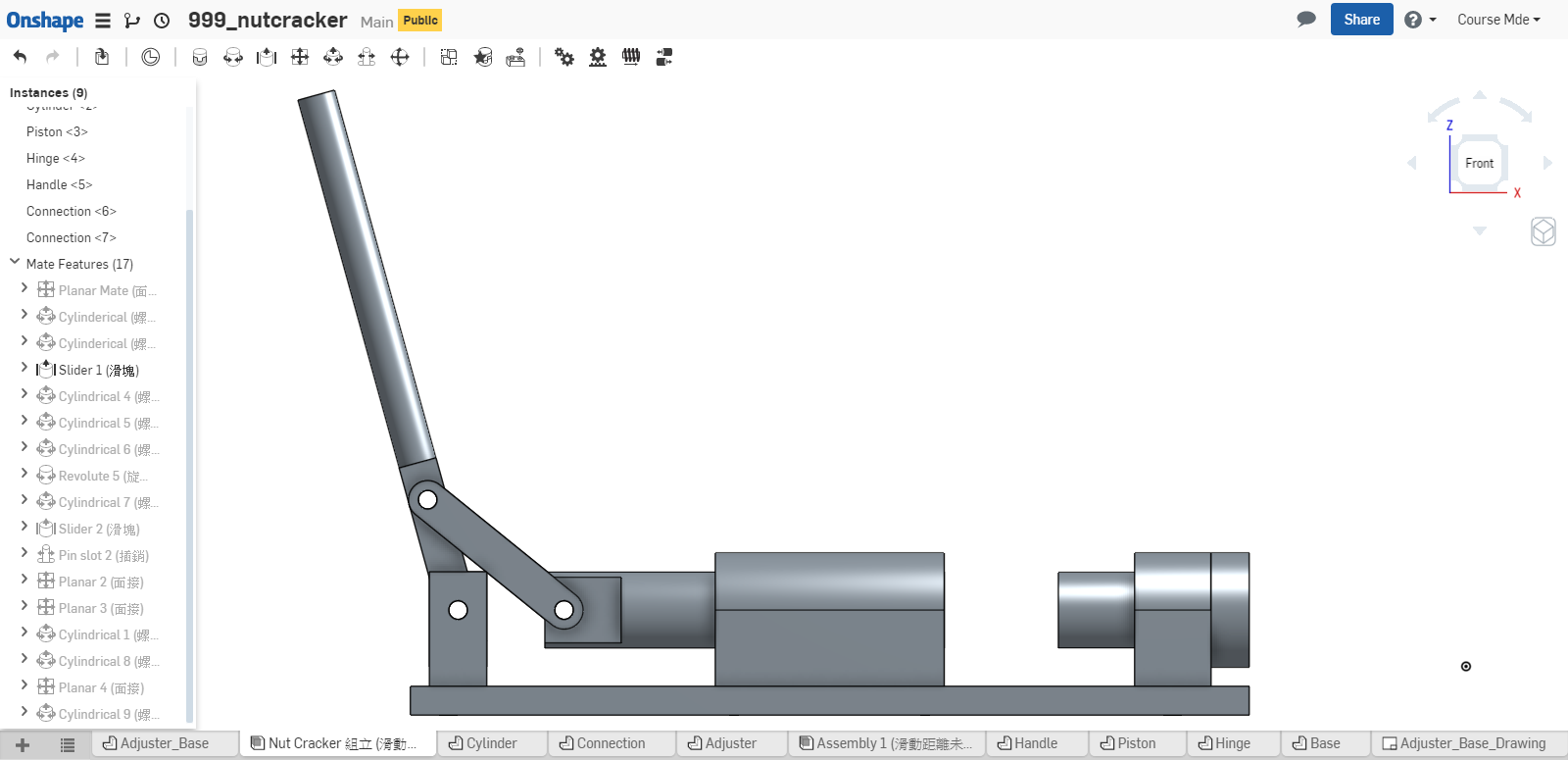
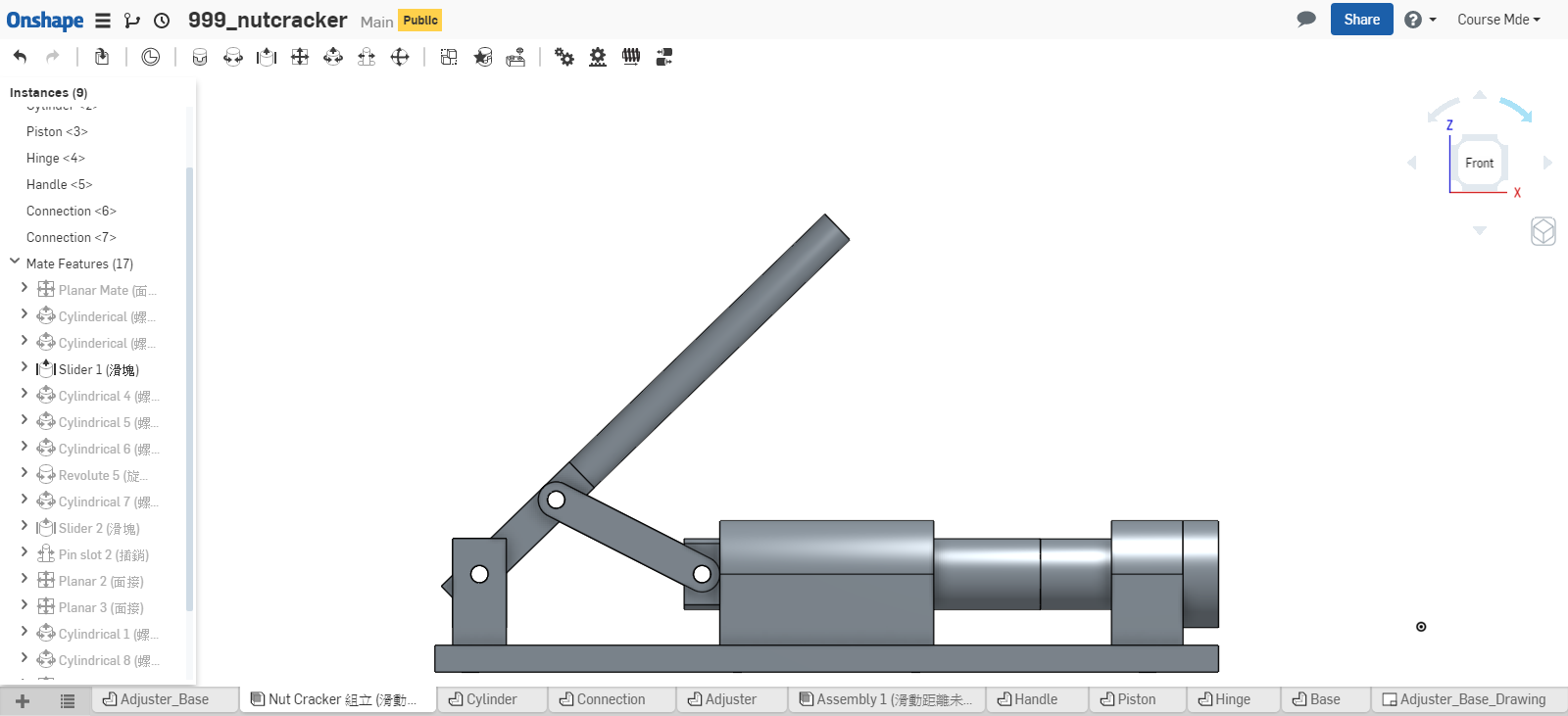
計算 Piston 不發生干涉的有效行程, 可採如下方法:
- 實際利用 Onshape 中的組立, 移動 piston 零件, 靠目測概略決定 piston 的有效行程. (目測法, 只能得到大概的行程範圍)
- 利用 Solvespace 繪製 2D 約束圖, 然後利用約束點在線或圓上的方式, 以圖解法解出有效行程, 如下圖一, 圖二與圖三所示. (圖解法, 利用 Solvespace 既有的約束條件設定完成計算)
- 利用 Jupyter 與 Python3 的 sympy 模組, 先進行符號式推導, 然後再利用數值分析解出 piston 的有效行程, 機構各點標示如下圖四所示, 計算出的 theta 轉角為 105.7, 如下圖五所示. (以自行編寫的 sympy 程式解題, 透過 Jupyterhub 可以有效進行協同設計運算)
- 除了上述的目測, 圖解與符號式結合數值分析法之外, 也可以採用基因演算法解題, 計算出的 theta 轉角為 105.7, 如下圖六所示. (利用演化法解題, 可以在單機運算, 也可以在 Jupyterhub 平台上進行運算)
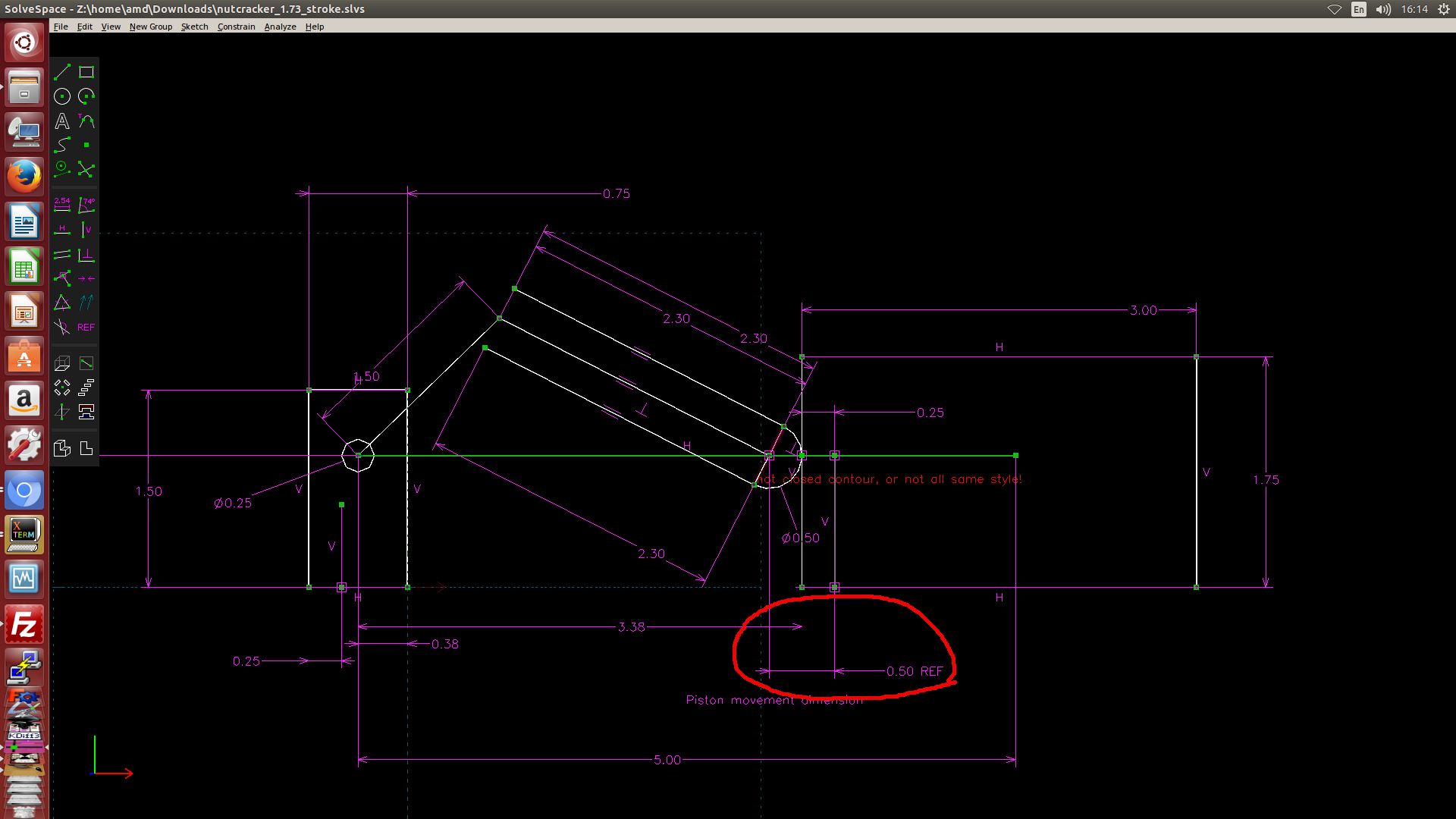
圖一: 利用 Solvespace 中的繪圖約束條件找出右邊的極限點距離 Onshape Piston 組立原點 0.5
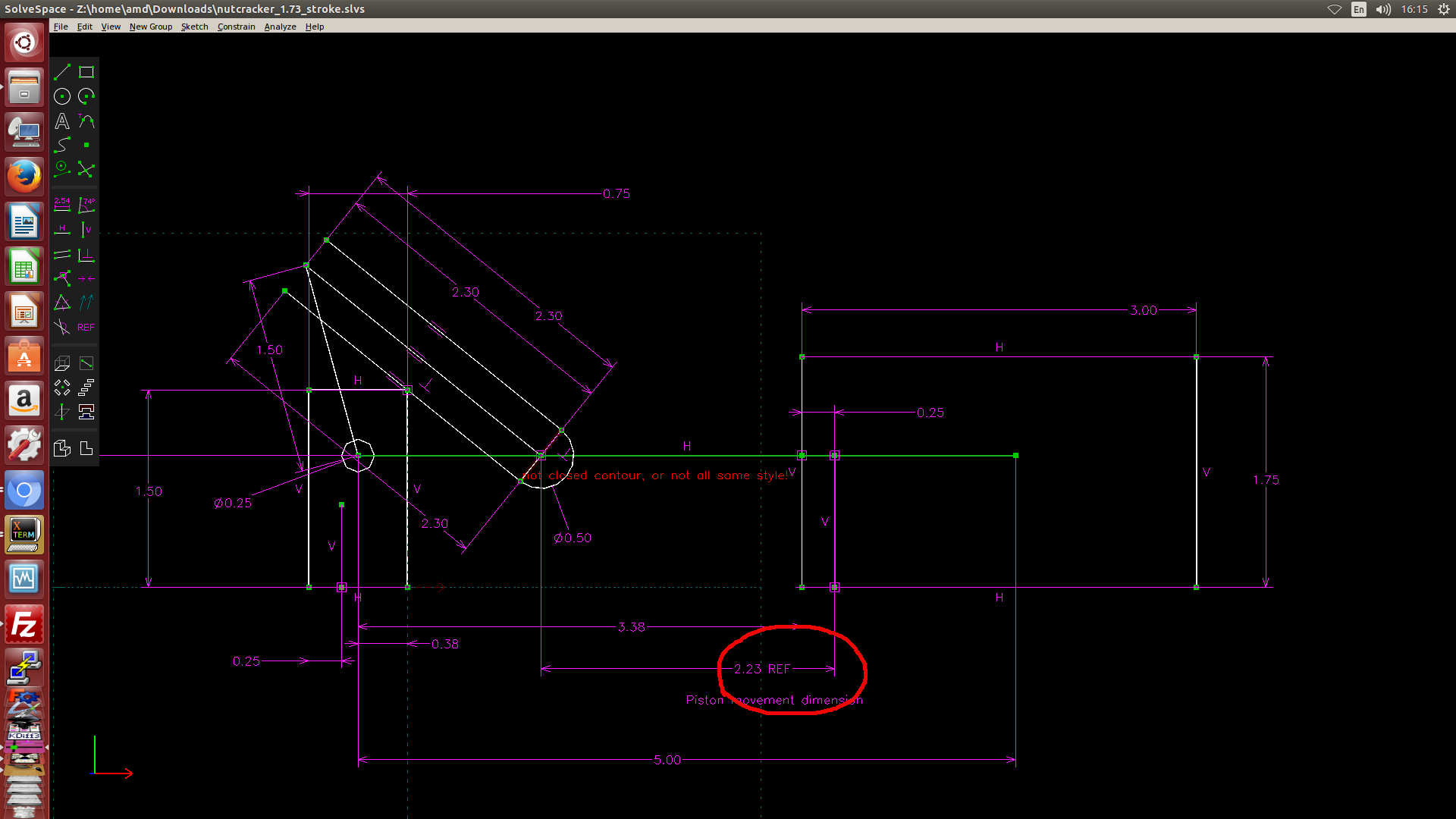
圖二: 利用 Solvespace 中的繪圖約束條件找出左邊的極限點距離 Onshape Piston 組立原點 2.23
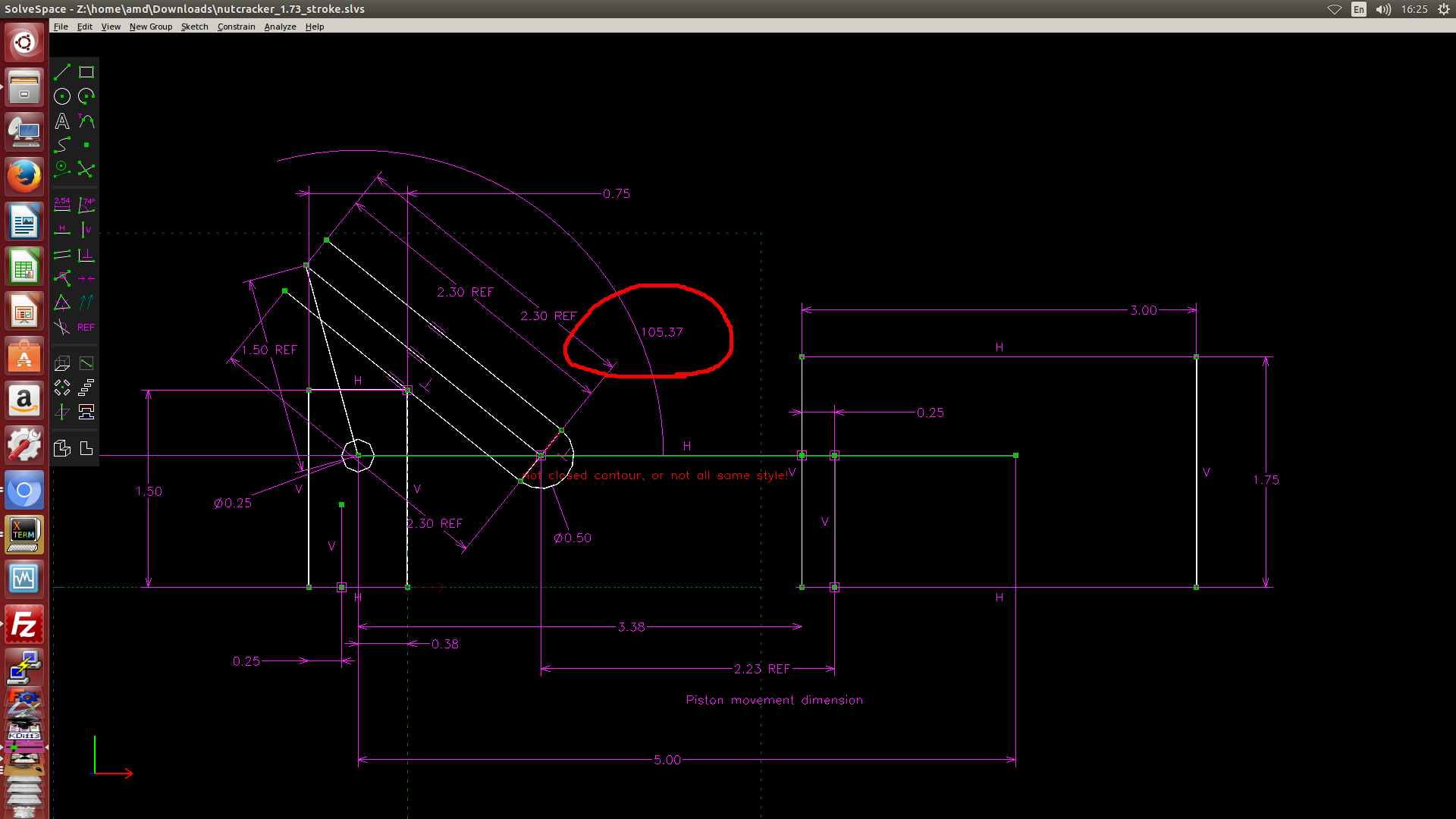
圖三: 當 piston 位於左邊極限點時, AB 轉角為 105.37 度
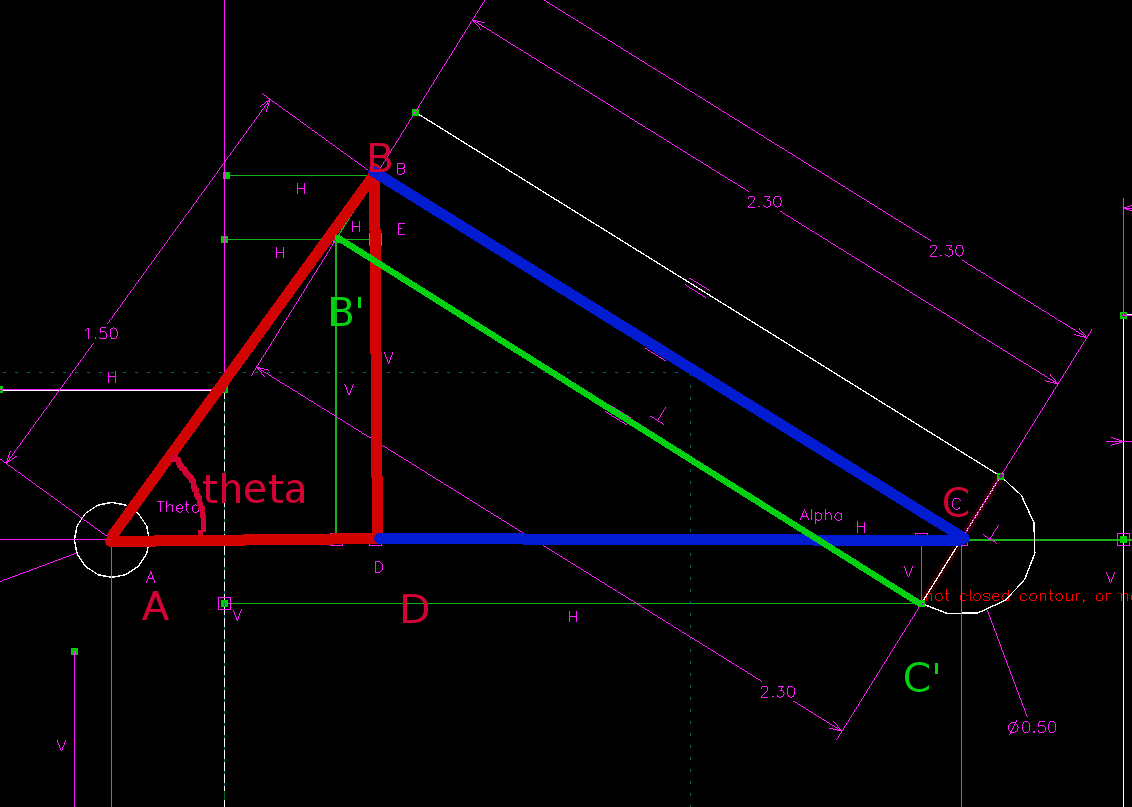
圖四: Jupyter 計算分析時機構各點標示圖
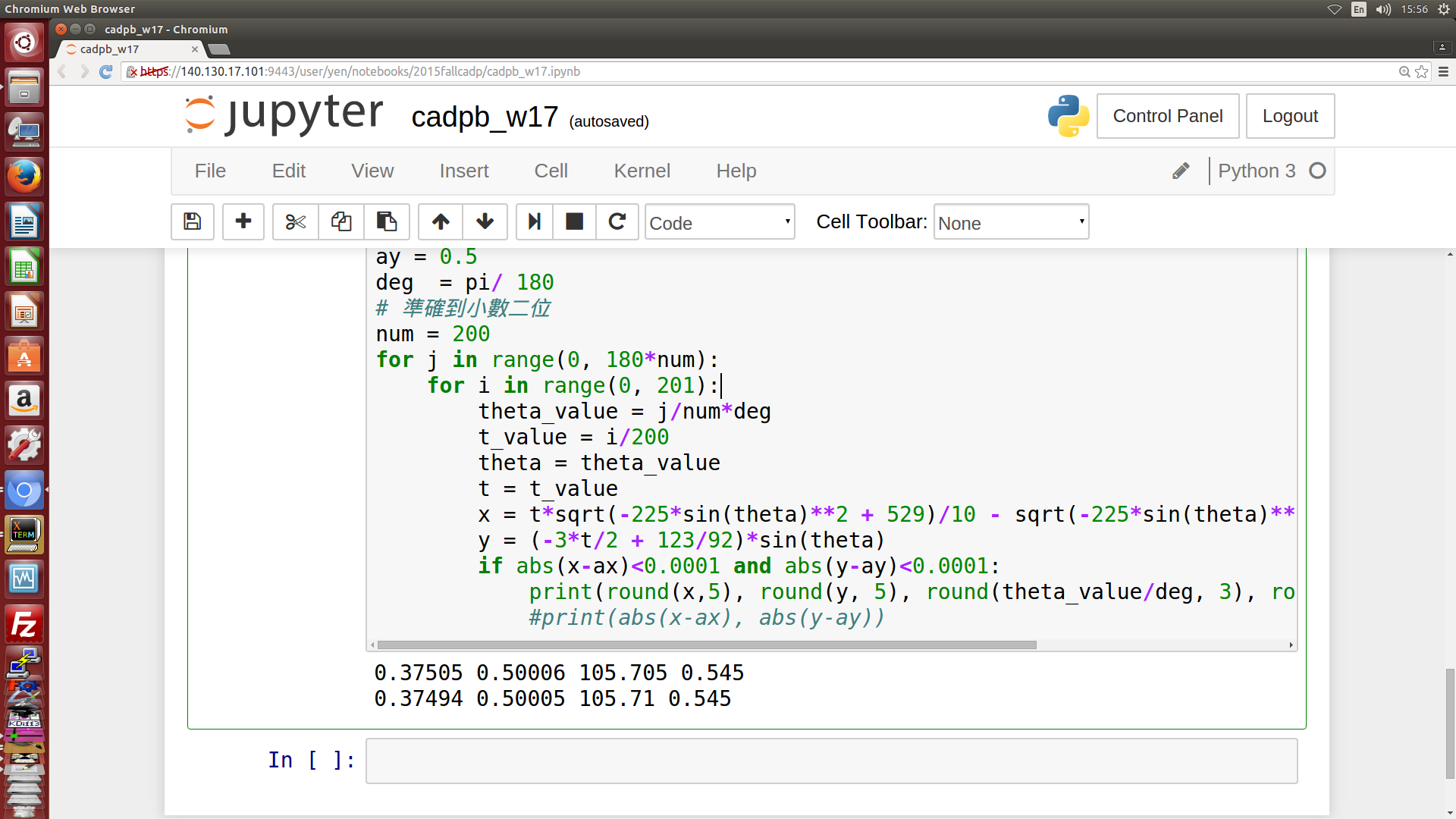
圖五: 利用 Jupyter 符號式結合數值分析法所得結果
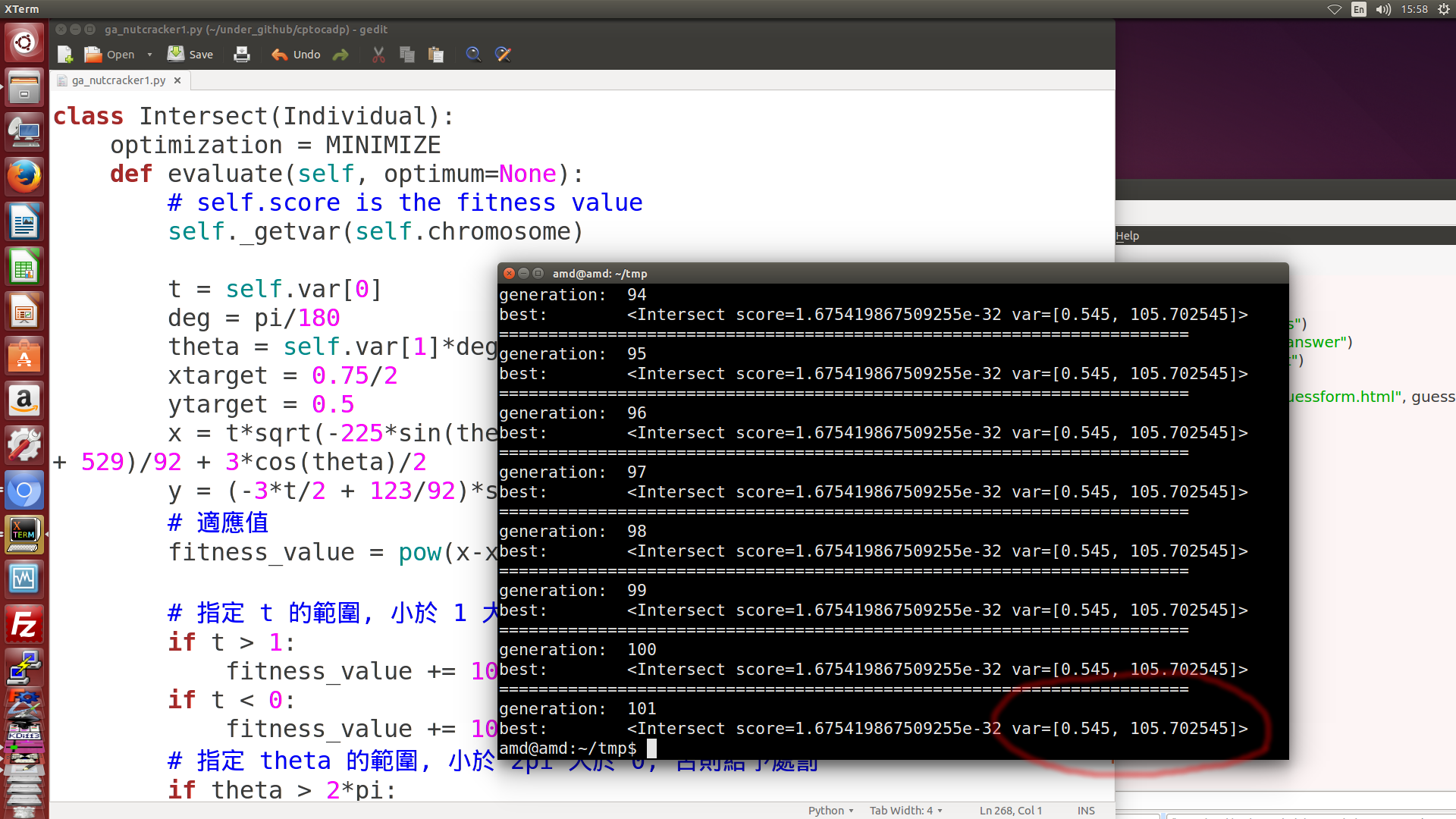
圖六: 利用基因演算解題, 所得到的結果, 當 piston 位於左邊極限點時, AB 轉角為 105.7 度
若採用 deap 與 numpy 解題 (AB 轉角極限為 105.71 度):
# 這裡採用 numpy 與 deap 模組解題, 使用 Genetic Algorithm 模式
# 解的問題為 Nutcracker 左邊 connect 轉角極限
import random
import array
from deap import base
from deap import creator
from deap import tools
import numpy
# for evalIntersect 函式中的 sqrt, sin, cos, pi
from math import *
# 1/4 最小化題目 type of problem
creator.create("FitnessMin", base.Fitness, weights=(-1.0,))
creator.create("Individual", array.array, typecode='d', \
fitness=creator.FitnessMin)
# 2/4 initilization
# 兩個變數題目
NDIM = 2
toolbox = base.Toolbox()
toolbox.register("attr_float", random.uniform, 0, 5)
toolbox.register("individual", tools.initRepeat, creator.Individual, toolbox.attr_float, NDIM)
toolbox.register("population", tools.initRepeat, list, toolbox.individual)
# 3/4 選擇 operator step3/4
toolbox.register("select", tools.selRandom, k=3)
# 也可以採用下列設定
#toolbox.register("mate", tools.cxTwoPoint)
#toolbox.register("mutate", tools.mutGaussian, mu=0, sigma=1, indpb=0.1)
#toolbox.register("select", tools.selTournament, tournsize=3, k=3)
def evalIntersect(individual):
t = individual[0]
deg = pi/180
theta = individual[1]*deg
xtarget = 0.75/2
ytarget = 0.5
x = t*sqrt(-225*sin(theta)**2 + 529)/10 - sqrt(-225*sin(theta)**2 \
+ 529)/92 + 3*cos(theta)/2
y = (-3*t/2 + 123/92)*sin(theta)
# 適應值
fitness_value = pow(x-xtarget, 8)+pow(y-ytarget, 8)
# 指定 t 的範圍, 小於 1 大於 0, 否則給予處罰
if t > 1:
fitness_value += 1000
if t < 0:
fitness_value += 1000
# 指定 theta 的範圍, 小於 2pi 大於 0, 否則給予處罰
if theta > 2*pi:
fitness_value += 1000
if theta < 0:
fitness_value += 1000
return fitness_value,
toolbox.register("evaluate", evalIntersect)
# 以上到 evaluate 為止, 為定義 operators
# 4/4 以下則為 Algorithms
def main():
# Differential evolution parameters
CR = 0.25
F = 1
MU = 300
NGEN = 200
pop = toolbox.population(n=MU);
hof = tools.HallOfFame(1)
stats = tools.Statistics(lambda ind: ind.fitness.values)
stats.register("avg", numpy.mean)
stats.register("std", numpy.std)
stats.register("min", numpy.min)
stats.register("max", numpy.max)
# Evaluate the individuals
fitnesses = toolbox.map(toolbox.evaluate, pop)
for ind, fit in zip(pop, fitnesses):
ind.fitness.values = fit
for g in range(1, NGEN):
for k, agent in enumerate(pop):
a,b,c = toolbox.select(pop)
y = toolbox.clone(agent)
index = random.randrange(NDIM)
for i, value in enumerate(agent):
if i == index or random.random() < CR:
y[i] = a[i] + F*(b[i]-c[i])
y.fitness.values = toolbox.evaluate(y)
if y.fitness > agent.fitness:
pop[k] = y
hof.update(pop)
print("Best individual is ", hof[0], hof[0].fitness.values[0])
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
上述課程資料與 Wordpress 網頁上的資料內容相同, Wordpress 網站屬於動態的網誌, 而 http://chiamingyen.github.io/kmolab/ 則是靜態網誌系統, 採用靜態網誌的優點如下:
- 比較安全
- 比較不會過時
- 部署成本比較低
- 可在各種平台上使用
- 各階段改版資料均有紀錄
以下為參考用的 GA 解 Nutcracker 題目的程式碼:
#encoding=utf8
# genetic.py
#
import random
import operator
# for Intersect
from math import *
MAXIMIZE, MINIMIZE = 11, 22
class Individual:
chromosome = None
score = None
# Here the size of var depends on var_number
var = []
var_number = 2
for i in range(var_number):
var.append(0)
alleles = (0,1)
# 以下為參數可負數時的編碼考量
#前10為小數,後10為整數,第21則為正負號
#0~9表示小數,10~19表示整數,而指標第20則表示第一數的正號或負號,若為0則表示正,若為1表示負號.
#21~30表示第二數的小數部分,31~40則表示第二數的整數部分,第41指標則表示第二數的正號或負號
#42~51表示第三數的小數部分,52~61則表示第二數的整數部分,第62指標則表示第三數的正號或負號
# -1023 ~ 1023
#length = 21*var_number,若接受負數參數,則必須同步修改 20->21
length = 20*var_number
seperator = ''
optimization = MINIMIZE
def __init__(self, chromosome=None):
self.chromosome = chromosome or self._makechromosome()
self.score = None # set during evaluation
def _getvar(self,chromosome=None):
x = 0
for i in range(0,self.var_number):
for j in range(i*20,i*20+10):
x +=self.chromosome[j]<<(j-(i*20))
if (x>999):
x=999
x/=1000.
for j in range(i*20+10,i*20+20):
x +=self.chromosome[j]<<(j-(i*20+10))
self.var[i] = x
return self.var
''' for -1023 ~ 1023,當設計變數可以接受負值時使用,每一變數使用21個 bit strings
#for design variable -1023 ~1023
for i in range(self.var_number):
x = 0
for j in range(i*21,i*21+10):
x +=self.chromosome[j]<<(j-(i*21))
if (x>999):
x=999
x/=1000.
for j in range(i*(21)+10,i*(21)+20):
x +=self.chromosome[j]<<(j-(i*21+10))
if(self.chromosome[i*(21)+20] == 1):
self.var[i] = -x
else:
self.var[i] = x
x = 0
return self.var
'''
def _makechromosome(self):
"makes a chromosome from randomly selected alleles."
return [random.choice(self.alleles) for gene in range(self.length)]
def evaluate(self, optimum=None):
"this method MUST be overridden to evaluate individual fitness score."
pass
def crossover(self, other):
"override this method to use your preferred crossover method."
return self._twopoint(other)
def mutate(self, gene):
"override this method to use your preferred mutation method."
self._pick(gene)
# sample mutation method
def _pick(self, gene):
"chooses a random allele to replace this gene's allele."
self.chromosome[gene] = random.choice(self.alleles)
# sample crossover method
def _twopoint(self, other):
"creates offspring via two-point crossover between mates."
left, right = self._pickpivots()
def mate(p0, p1):
chromosome = p0.chromosome[:] # 交配時,以p0的基因為基礎(複製整個 p0 的染色體內容
chromosome[left:right] = p1.chromosome[left:right] # 接續上一個 p0 的染色體內容,將索引 left 至 right 的內容,替換成 p1 的基因
#child = p1.__class__(chromosome) 這是原先的程式,但是應該子代要指向 p0 的內容才對
child = p0.__class__(chromosome)
child._repair(p0, p1)
return child
return mate(self, other), mate(other, self)
# some crossover helpers ...
def _repair(self, parent1, parent2):
"override this method, if necessary, to fix duplicated genes."
pass
def _pickpivots(self):
left = random.randrange(1, self.length-2)
right = random.randrange(left, self.length-1)
return left, right
#
# other methods
#
def __repr__(self):
"returns string representation of self"
'''
return '<%s chromosome="%s" score=%s var=%s>' % \
(self.__class__.__name__,
self.seperator.join(map(str,self.chromosome)), self.score,self._getvar(self.chromosome))
'''
return '<%s score=%s var=%s>' % \
(self.__class__.__name__,self.score,self._getvar(self.chromosome))
# since the __cmp__ special function is gone use the __lt__ in stead
# use the expression (a > b) - (a < b) as the equivalent for cmp(a, b)
#def __cmp__(self, other):
# these are for python 3
def __cmp__(self, other):
if self.optimization == MINIMIZE:
#return cmp(self.score, other.score)
return (self.score > other.score) - (self.score < other.score)
else: # MAXIMIZE
#return cmp(other.score, self.score)
return (other.score > self.score) - (other.score < self.score)
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.__cmp__(other) < 0
def __le__(self, other):
return self.__cmp__(other) <= 0
def __gt__(self, other):
return self.__cmp__(other) > 0
def __ge__(self, other):
return self.__cmp__(other) >= 0
def copy(self):
twin = self.__class__(self.chromosome[:])
twin.score = self.score
return twin
class Environment(object):
x = [0]
y = [0]
def __init__(self, kind, population=None, size=100, maxgenerations=100,
crossover_rate=0.90, mutation_rate=0.07, optimum=None):
self.kind = kind
self.size = size
self.optimum = optimum
self.population = population or self._makepopulation()
for individual in self.population:
individual.evaluate(self.optimum)
self.crossover_rate = crossover_rate
self.mutation_rate = mutation_rate
self.maxgenerations = maxgenerations
self.generation = 0
self.report()
def _makepopulation(self):
return [self.kind() for individual in range(self.size)]
def run(self):
while not self._goal():
self.step()
def _goal(self):
return self.generation > self.maxgenerations or \
self.best.score == self.optimum
def step(self):
# this sort is not working with python 3.0, modification is needed
self.population.sort()
self._crossover()
self.generation += 1
self.report()
self.x.append(self.generation)
# 設定為只附加所選定範圍的值,這裡只取大於或等於 0 的 score 值
if self.best.score <=5:
self.y.append(self.best.score)
else:
self.y.append(5)
def _crossover(self):
next_population = [self.best.copy()]
while len(next_population) < self.size:
mate1 = self._select()
if random.random() < self.crossover_rate:
mate2 = self._select()
offspring = mate1.crossover(mate2)
else:
offspring = [mate1.copy()]
for individual in offspring:
self._mutate(individual)
individual.evaluate(self.optimum)
next_population.append(individual)
self.population = next_population[:self.size]
def _select(self):
"override this to use your preferred selection method"
return self._tournament()
def _mutate(self, individual):
for gene in range(individual.length):
if random.random() < self.mutation_rate:
individual.mutate(gene)
#
# sample selection method
#
def _tournament(self, size=8, choosebest=0.90):
competitors = [random.choice(self.population) for i in range(size)]
competitors.sort()
if random.random() < choosebest:
return competitors[0]
else:
return random.choice(competitors[1:])
def best():
doc = "individual with best fitness score in population."
def fget(self):
return self.population[0]
return locals()
best = property(**best())
def report(self):
print ("="*70)
print ("generation: ", self.generation)
print ("best: ", self.best)
# 以上為 genetic.py 目前將兩者結合在一起
#encoding=utf8
# volume.py - useage example
#
# the fittest individual will have a chromosome consisting of 40 '1's
#
#
#import genetic
#此一加總函式在 volume 最大化中,並未使用
def sum(seq):
def add(x,y): return x+y
return reduce(add, seq, 0)
class Volume(Individual):
optimization = MAXIMIZE
def evaluate(self, optimum=None):
SURFACE = 80
# self.score is the fitness value
self._getvar(self.chromosome)
x = self.var[0]
y = self.var[1]
z=(SURFACE - x*y)/(2.*(x+y))
fitness_value = x*y*z
self.score = fitness_value
def mutate(self, gene):
self.chromosome[gene] = not self.chromosome[gene] # bit flip
class Intersect(Individual):
optimization = MINIMIZE
def evaluate(self, optimum=None):
# self.score is the fitness value
self._getvar(self.chromosome)
t = self.var[0]
deg = pi/180
theta = self.var[1]*deg
xtarget = 0.75/2
ytarget = 0.5
x = t*sqrt(-225*sin(theta)**2 + 529)/10 - sqrt(-225*sin(theta)**2 + 529)/92 + 3*cos(theta)/2
y = (-3*t/2 + 123/92)*sin(theta)
# 適應值
fitness_value = pow(x-xtarget, 8)+pow(y-ytarget, 8)
# 指定 t 的範圍, 小於 1 大於 0, 否則給予處罰
if t > 1:
fitness_value += 1000
if t < 0:
fitness_value += 1000
# 指定 theta 的範圍, 小於 2pi 大於 0, 否則給予處罰
if theta > 2*pi:
fitness_value += 1000
if theta < 0:
fitness_value += 1000
self.score = fitness_value
def mutate(self, gene):
self.chromosome[gene] = not self.chromosome[gene] # bit flip
if __name__ == "__main__":
#env = Environment(Volume, size=500, maxgenerations=100)
env = Environment(Intersect, size=500, maxgenerations=100)
env.run()